A disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface a speed undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with an identical stationary disk B. Find the velocity of the disk B after
4.9 (71) In stock

Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:a disk a of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v 2
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ A disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface a speed undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with an identical stationary disk B- Find the velocity of the disk B after collision the impact parameter is r-2 as shown in the figure 1- VYT

3.5b Ex4 ON17 P23 Q3 Ball 2D Collision, AS Dynamics
A ball with a mass of 2 kg traveling at 8 m/s strikes a ball of mass 4 kg traveling 2m/s. After collision, both balls move at the same velocity (v). What

A disk sliding with velocity u on a smooth horizontal plane strikes another identical disk kept at rest as shown in the figure. If the impact between - Sarthaks eConnect
Class 11 : exercise-1 : Disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v collides elastically with an
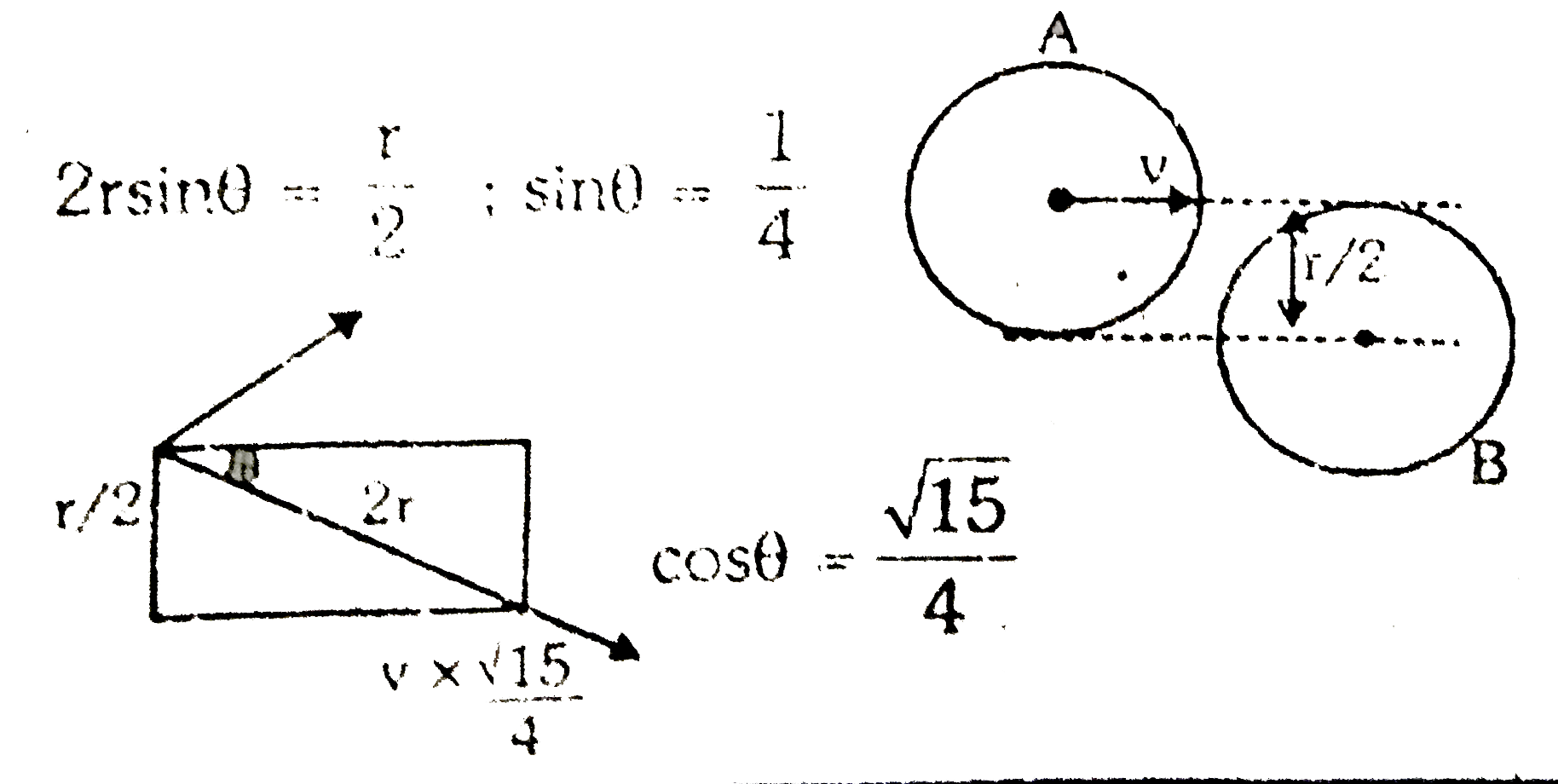
A disk A of radious r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v

A disk A of radious r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v undergoes an elastic colli
Ask the Physicist!

Solution] As shown below, a ball of mass m with an …

TU and B of radius r are to 28. Two identical spheres A and B of radius simultaneously from the positions as showi of radius (R + r) and which moves on

Two objects of the same mass and with the same initial speed moving in a horizontal plane collide and move away together at half their initial speeds after the collision The angle
A disk of mass M and radius R is initially rotating at angular velocity of ω. While rotating, it is placed on a horizontal surface whose coefficient of friction is μ= 0.5.

8.3 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions

A disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface a speed undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with an identical stationary disk B. Find the velocity of the disk B after

A disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface a speed undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with an identical stationary disk B. Find the velocity of the disk B after
Perfectly Smooth Buttercream Recipe - American Cake Decorating
The best paint brushes for a perfectly smooth paint finish
Spectral reflectivity of perfectly smooth metal surfaces [3
 hikes Prime membership fees in U.S. as wages, costs rise
hikes Prime membership fees in U.S. as wages, costs rise Pilates Lifestyle Simple Everyday - The Simple Everyday
Pilates Lifestyle Simple Everyday - The Simple Everyday Breathable Fashion Young Girls Briefs Sexy Lace Transparent Ladies Cotton Panties - Expore China Wholesale Women's Briefs and Women's Underwear, Women's Briefs
Breathable Fashion Young Girls Briefs Sexy Lace Transparent Ladies Cotton Panties - Expore China Wholesale Women's Briefs and Women's Underwear, Women's Briefs Comfortable Lightly Lined Wireless and Non Padded Brown Bra
Comfortable Lightly Lined Wireless and Non Padded Brown Bra Mens Organic Cotton Trunks
Mens Organic Cotton Trunks Primeiro avião do mundo específico para atletas é apresentado na
Primeiro avião do mundo específico para atletas é apresentado na