How do you prove sin(90°-a) = cos(a)?
4.7 (437) In stock
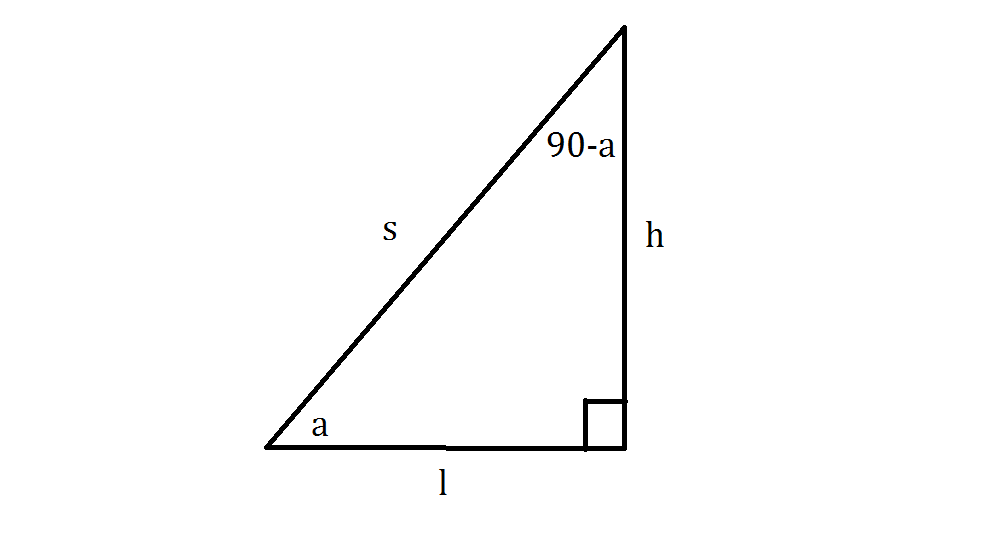
I prefer a geometric proof. See below. If you're looking for a rigorous proof, I'm sorry - I'm not good at those. I'm sure another Socratic contributor like George C. could do something a little more solid than I can; I'm just going to give the lowdown on why this identity works. Take a look at the diagram below: It's a generic right triangle, with a 90^o angle as indicated by the little box and an acute angle a. We know the angles in a right triangle, and a triangle in general, must add to 180^o, so if we have an angle of 90 and an angle of a, our other angle must be 90-a: (a)+(90-a)+(90)=180 180=180 We can see that the angles in our triangle do indeed add to 180, so we're on the right track. Now, let's add some variables for side length onto our triangle. The variable s stands for the hypotenuse, l stands for length, and h stands for height. We can start on the juicy part now: the proof. Note that sina, which is defined as opposite (h) divided by hypotenuse (s) , equals h/s in the diagram: sina=h/s Note also that the cosine of the top angle, 90-a, equals the adjacent side (h) divided by the hypotenuse (s): cos(90-a)=h/s So if sina=h/s, and cos(90-a)=h/s Then sina must equal cos(90-a)! sina=cos(90-a) And boom, proof complete.

Solved Prove the identity. sin(90° + x) + sin(90° - x) = 2

Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples

prove that sin A/sin(90-A) + cos A/cos(90-A) = sec A cosec A

In triangle ABC angle C = 90 degrees Prove That, [(1 - sin A)/(1 +
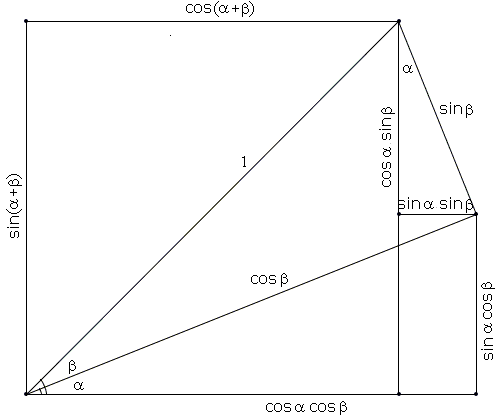
Addition and Subtraction Formulas for Sine and Cosine
Prove that:sin(90+theta )=costheta

SIN 90° - FORMULA, DERIVATION AND EXAMPLES - mydomain
Sin( 90 theta ) = cos theta prove this using coordinate axes

Prove that Sin (90 + x) = Cos x - Maths - Introduction to

Answered: QUESTION 5 5.1 Simplify fully: sin(90°…
How do you find the exact value of sin(-90)?
sin (90-x) = 12/13 what is the value of sin x? – PWN Test Prep
6. sin150 Sin(90+60)=+cos60∘=+1/2 sin(180−30)=+sin30∘+1/2
Sine/Cosine Approximations Simplify Controller Operation
Proof of the reduction Formulas for angles (90°+α) or (π/2+α)
 Gaiam Gaiam Grey Grippy Yoga Socks - Sportausrüstung
Gaiam Gaiam Grey Grippy Yoga Socks - Sportausrüstung Moms for Liberty Has Created Nightmares for Schools Across the Country
Moms for Liberty Has Created Nightmares for Schools Across the Country Wizard robe, black-red
Wizard robe, black-red Scarlet Slip Dress - Black - xs
Scarlet Slip Dress - Black - xs Slenderman Masky Hoodie Creepypasta Set of 3 signed Prints Chris Oz Fulton
Slenderman Masky Hoodie Creepypasta Set of 3 signed Prints Chris Oz Fulton Just Sexy Lingerie Flyaway Babydoll with Lace, Women's Lingerie Set
Just Sexy Lingerie Flyaway Babydoll with Lace, Women's Lingerie Set