physical chemistry - Is the compressibility factor smaller or greater than 1 at low temperature and high pressure? - Chemistry Stack Exchange
4.6 (225) In stock

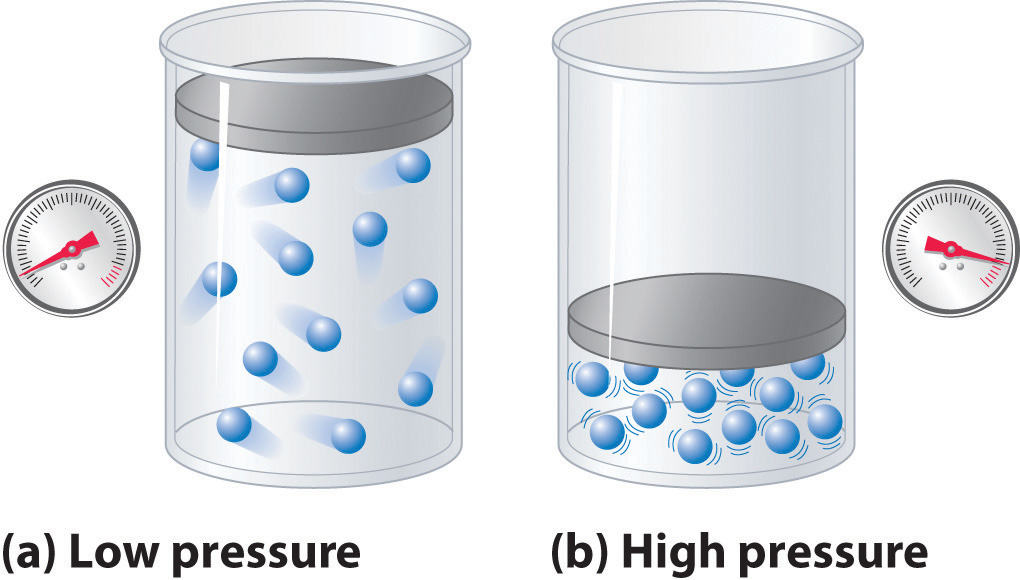
The compressibility factor of a gas is defined as $Z = pV/(nRT)$. If attractive intermolecular forces dominate then $Z$ tends to be smaller than 1, and vice versa if repulsive forces dominate. In
Effect of pulse-current-based protocols on the lithium dendrite

physical chemistry - Why do some gases have lower value of Z for a
The Behavior of Real Gases

Preliminary Chemical Engineering Plant Design - William - Ventech!

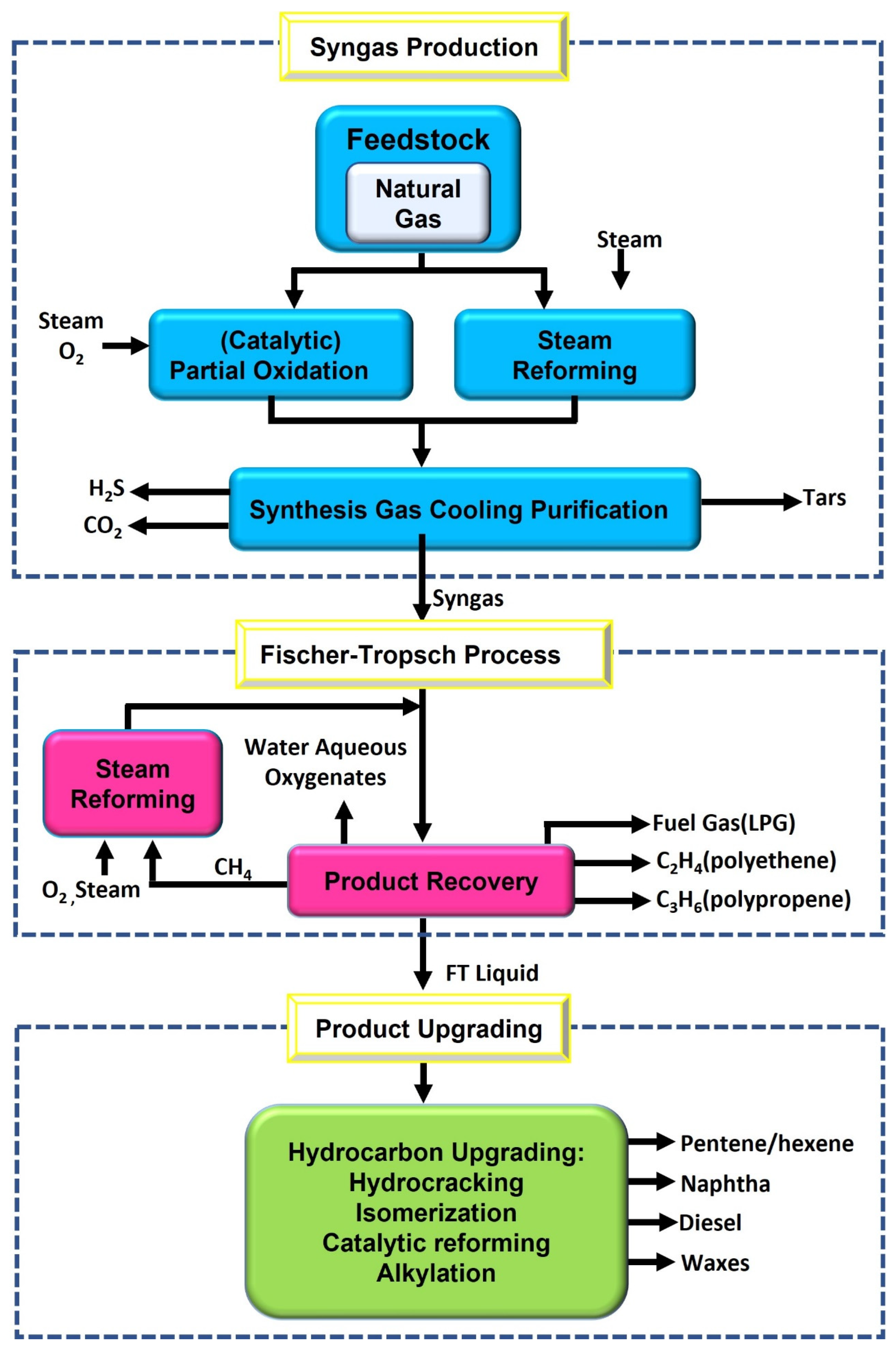
Sustainability, Free Full-Text
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior Chemistry: Atoms First

physical chemistry - why is the pressure exerted by ideal gas on
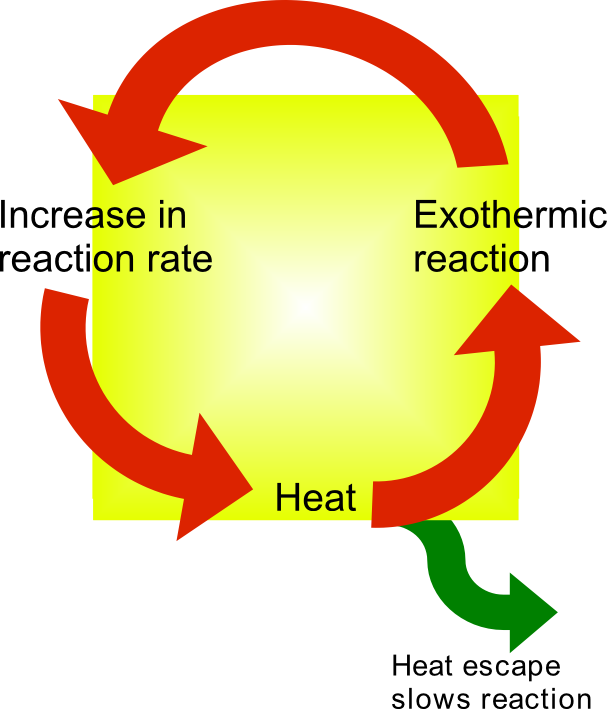
Thermal runaway - Wikipedia

What Exactly is The Compressibility of Fluids?
Why does water compress more than other gases? - Quora

Strain engineering of two‐dimensional materials: Methods

gas laws - Graph of compressibility factor vs pressure when real
Methane, Free Full-Text

physical chemistry - Why is the excluded volume in van der Waals 4
Compressibility Factor of Gas Overview, Equation & Chart
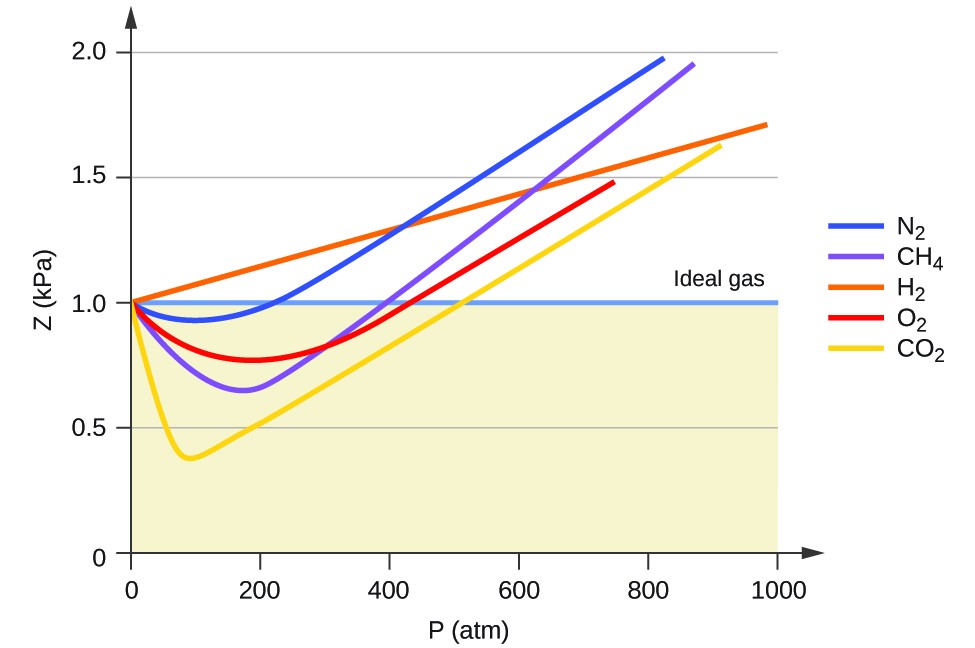
Compressibility factor Z = PV / nRT is plotted against pressure as
Compressibility factor (Z) is plotted against pressure at different te
 Silicone Body Hip Pads Butt Enhance Pads Body Shaper Crossdressers Drag Queen
Silicone Body Hip Pads Butt Enhance Pads Body Shaper Crossdressers Drag Queen Women Jean Shorts Girls Jeans Jeans For Teen Girls High Waist Fashion Teen Girls Girls Jeans Preppy Clothes Fashion Trendy Sexy Streetwear Teen Girls Lounge Shorts Ripped Shorts Leggings
Women Jean Shorts Girls Jeans Jeans For Teen Girls High Waist Fashion Teen Girls Girls Jeans Preppy Clothes Fashion Trendy Sexy Streetwear Teen Girls Lounge Shorts Ripped Shorts Leggings Landon Silver Fox Fur Parka – The Fancy Success
Landon Silver Fox Fur Parka – The Fancy Success MAX Washed Cropped Dungarees, Max, Ramanathapuram
MAX Washed Cropped Dungarees, Max, Ramanathapuram NIEUWE BMW i7 “PURE LUXE EDITION XDRIVE60 VAN AMICE FLORIS WYERS, IN-DEPTH WALK AROUND
NIEUWE BMW i7 “PURE LUXE EDITION XDRIVE60 VAN AMICE FLORIS WYERS, IN-DEPTH WALK AROUND Mary Wollstonecraft was more than a pair of knockers
Mary Wollstonecraft was more than a pair of knockers