Diabetic medications and major congenital malformations
4.5 (773) In stock

ABSTRACT The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing. T2DM is more common in patients with psychiatric disorders and those who take certain psychotropic drugs. T2DM occurs in 2%–7% of women of reproductive age. The prevalence of pregestational diabetes is 0.5%–2.4%, and that of gestational diabetes is 7%–28%, depending on geographical region. About 20%–50% of pregnancies, across the world, are unplanned; this figure is higher, at about 65%, in women with psychiatric disorders. As a result, many women of reproductive age who have diabetes, including women who do not know that they have diabetes, may unintentionally become pregnant, thus unknowingly exposing their pregnancy to diabetes and its treatment. Exposure of pregnancy to pregestational and gestational diabetes is associated with risks to the mother as well as risks to the child. Risks to the mother include obesity, hypertension, and preeclampsia. Risks to the child include spontaneous abortion, fetal death, macrosomia, major congenital malformations (MCMs), preterm delivery, neonatal hypoglycemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. A recent large retrospective cohort study with data from 6 countries in Europe, Asia, and North America found that, in about 51,000 women with pregestational T2DM, neither MCMs nor cardiac malformations were more prevalent in offspring of children periconceptionally exposed to second-line antidiabetic treatments relative to exposure to insulin. These findings are reassuring but have limitations that are discussed. A reasonable conclusion from a reading of the reviewed literature is that pregestational and gestational diabetes are best treated during pregnancy, that insulin is a first-line treatment, that metformin is an increasingly accepted alternative, and that safety data on second-line antidiabetic treatments are, so far, reassuring. J Clin Psychiatry 2024;85(1):24f15318 Author affiliations appear at the end of this article
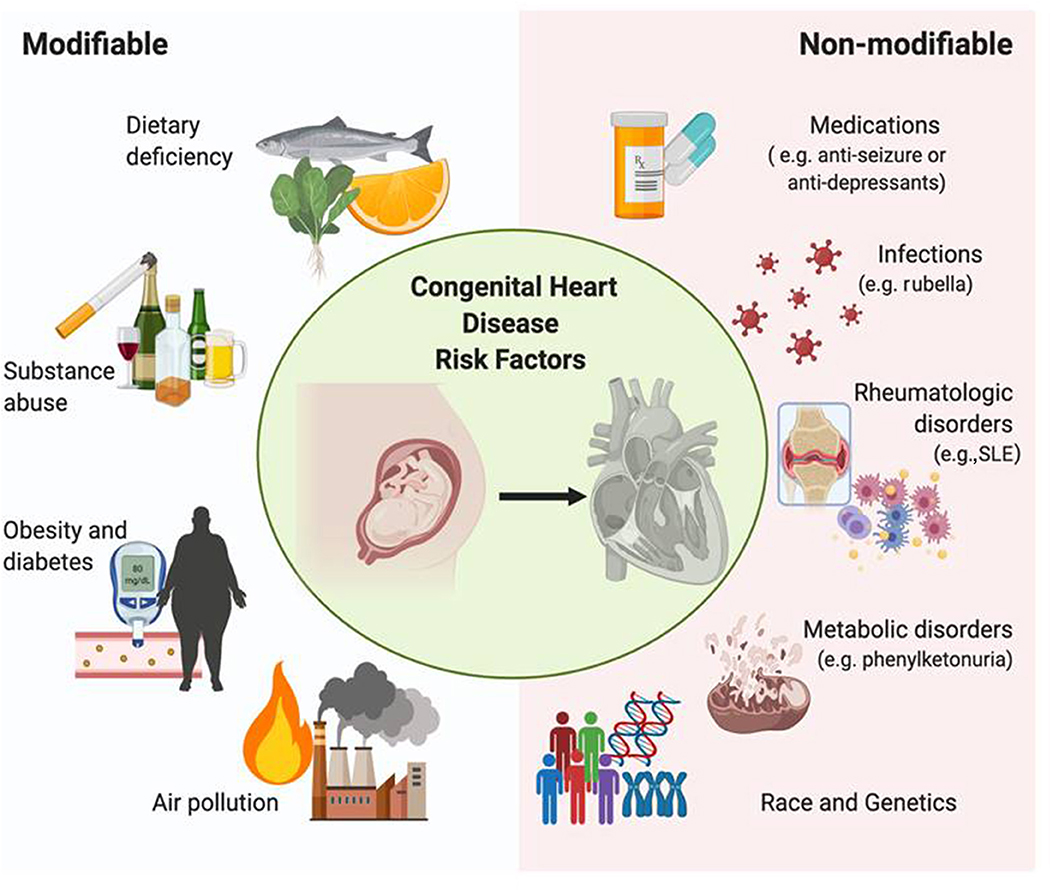
Frontiers Race and Genetics in Congenital Heart Disease
Clinical and Practical Psychopharmacology

PDF] Comparative risk of major congenital malformations with eight different antiepileptic drugs: a prospective cohort study of the EURAP registry

Diabetes mellitus: Classification, mediators, and complications; A
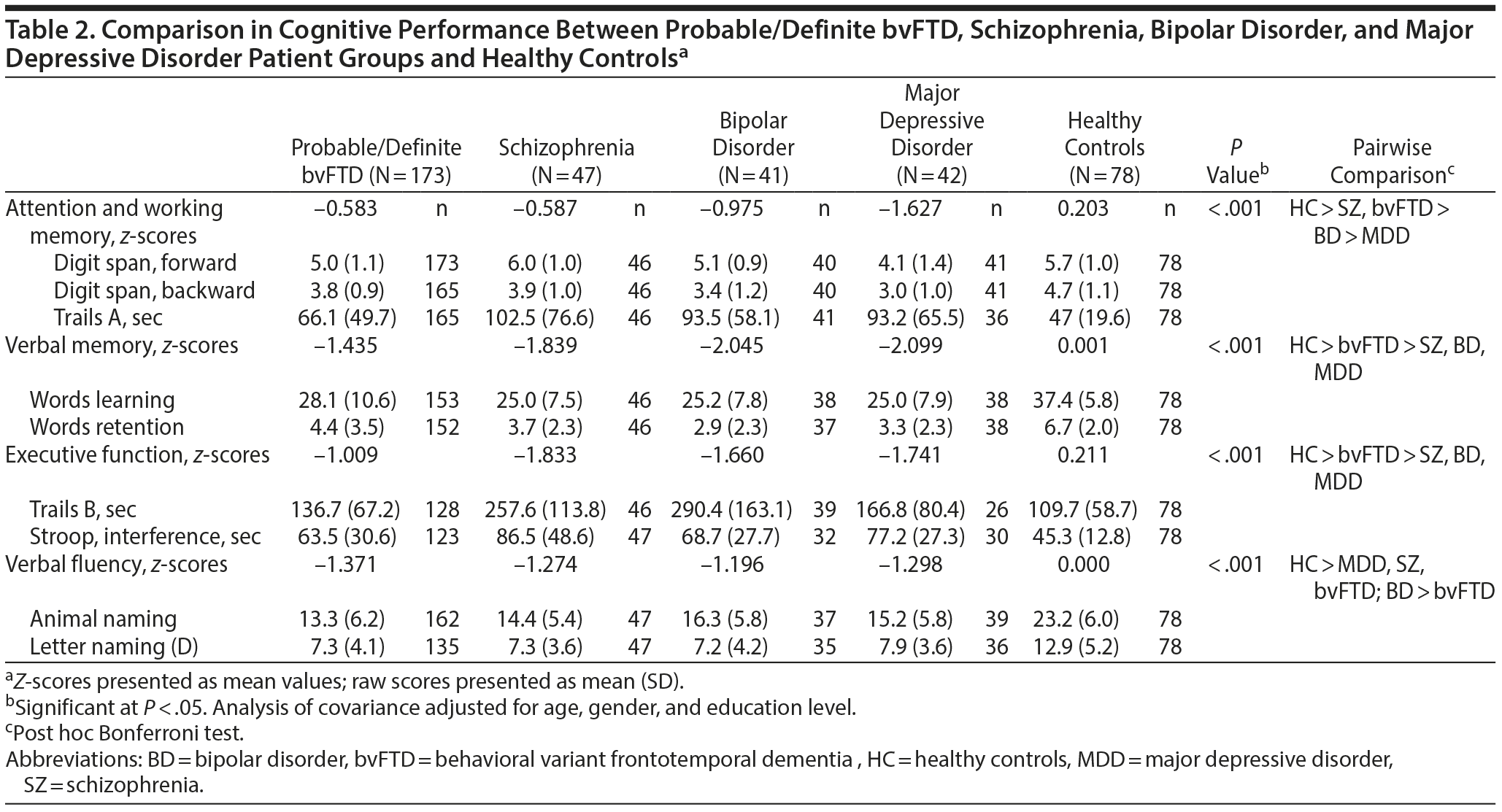
Cognitive Deficits in Patients With Neuropsychiatric Symptoms: A Comparative Study Between Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia and Primary Psychiatric Disorders
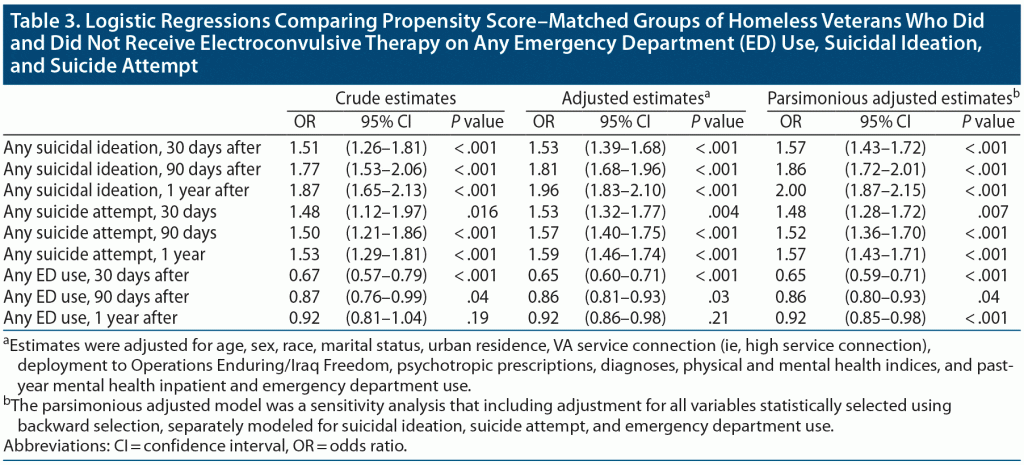
Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy on Suicidal Behavior and Emergency Department Use Among Homeless Veterans: A Propensity Score–Matched Study

Major Congenital Malformations Among The Newborns in BSMMU Hospital

Gestational diabetes - Wikipedia
The Pathogenesis of Congenital Anomalies: Roles of Teratogens and

Identifying Specific Clinical Symptoms of Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia Versus Differential Psychiatric Disorders in Patients Presenting With a Late-Onset Frontal Lobe Syndrome

11 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs

Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Practice Essentials
23 Maternity Photography ideas jcpenney portraits, maternity
Maternity Photos in Tacoma-Puyallup - Harmony Photography
White Mark Plus Maternity Womens Scoop Neck 3/4 Sleeve Tunic Top
 BRASIER COPA B INDIVIDUAL BASICO BEIGE – LiliPink Costa Rica
BRASIER COPA B INDIVIDUAL BASICO BEIGE – LiliPink Costa Rica Hanes Originals Women’s Bikini Underwear, Breathable Cotton Stretch, 6-Pack
Hanes Originals Women’s Bikini Underwear, Breathable Cotton Stretch, 6-Pack- Purple brand jeans (Made in Italy edition (black tags ) Worn great
 Nursing Bras for Breastfeeding Maternity Bra Push Up Deep V Neck Seamless Clip Down
Nursing Bras for Breastfeeding Maternity Bra Push Up Deep V Neck Seamless Clip Down- Plus Size - Retro Cherries Lace Longline Bra - Torrid
 Petite Coquette Studs
Petite Coquette Studs

