How do 24-h movement behaviours change during and after vacation
4.6 (780) In stock
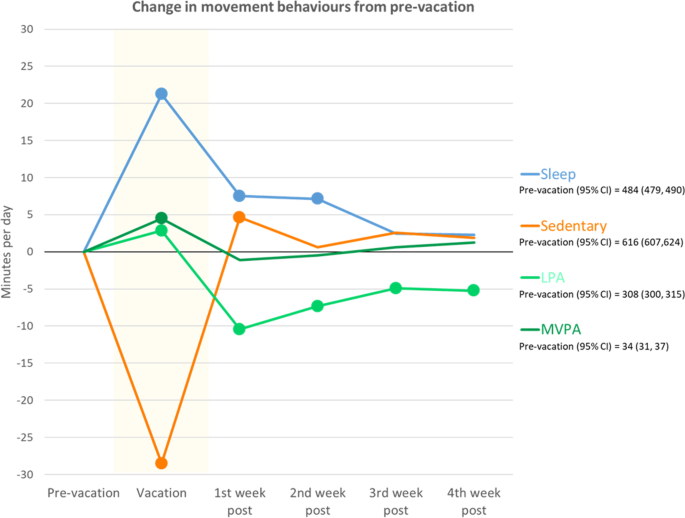
For adults, vacations represent a break from daily responsibilities of work – offering the opportunity to re-distribute time between sleep, sedentary behaviour, light physical activity (LPA) and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) across the 24-h day. To date, there has been minimal research into how activity behaviour patterns change on vacation, and whether any changes linger after the vacation. This study examined how daily movement behaviours change from before, to during and after vacations, and whether these varied based on the type of vacation and vacation duration. Data collected during the Annual Rhythms In Adults’ lifestyle and health (ARIA) study were used. 308 adults (mean age 40.4 years, SD 5.6) wore Fitbit Charge 3 fitness trackers 24 h a day for 13 months. Minute-by-minute movement behaviour data were aggregated into daily totals. Multi-level mixed-effects linear regressions were used to compare movement behaviours during and post-vacation (4 weeks) to pre-vacation levels (14 days), and to examine the associations with vacation type and duration. Participants took an average of 2.6 (SD = 1.7) vacations of 12 (SD = 14) days’ (N = 9778 days) duration. The most common vacation type was outdoor recreation (35%) followed by family/social events (31%), rest (17%) and non-leisure (17%). Daily sleep, LPA and MVPA all increased (+ 21 min [95% CI = 19,24] p < 0.001, + 3 min [95% CI = 0.4,5] p < 0.02, and + 5 min [95% CI = 3,6] p < 0.001 respectively) and sedentary behaviour decreased (-29 min [95% CI = -32,-25] p < 0.001) during vacation. Post-vacation, sleep remained elevated for two weeks; MVPA returned to pre-vacation levels; and LPA and sedentary behaviour over-corrected, with LPA significantly lower for 4 weeks, and sedentary behaviour significantly higher for one week. The largest changes were seen for “rest” and “outdoor” vacations. The magnitude of changes was smallest for short vacations (< 3 days). Vacations are associated with favourable changes in daily movement behaviours. These data provide preliminary evidence of the health benefits of vacations. The study was prospectively registered on the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry (Trial ID: ACTRN12619001430123).

Canada's First 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Adults

How to Break Bad Habits and Change Behaviors
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/manpackingsuitcase-573cccae3df78c6bb05a6489.jpg)
6 Healthy Travel Tips to Maintain Fitness and Nutrition Goals, According to a Personal Trainer
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1281577448-10051ada7d174f3faad83625c57099ea.jpg)
This Is How Many Vacation Days You Should Take to Stay Healthy, According to New Research

Post-exertional malaise - MEpedia

How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System?

Springer Nature research repository - Categories
New Study Reveals That a Four-Day Work Week Can Improve Health

How Your Menstrual Cycle Affects Your Behavior

The whole day matters: Understanding 24-hour movement guideline adherence and relationships with health indicators across the lifespan - ScienceDirect

为什么休假对健康有益?这项队列研究提供了一些证据- 医咖会

24-hour movement guidelines – children and young people (5 to 17 years) – brochure

Change in movement behaviours from pre-vacation by type of vacation.

Springer Nature research repository - Categories
Lululemon In Movement Tight 25 *Everlux - Black - lulu fanatics
- 🌹 VENDOR SPOTLIGHT 🌹 @cantiq.losangeles is a handmade lingerie
 Leica Q3 vs Q2 Comparison: What is new and is it worth upgrading?
Leica Q3 vs Q2 Comparison: What is new and is it worth upgrading? Buy Calvin Klein Women's CK One Cotton Lightly Lined Demi Bra, Mini Staggered Logo Print, 34D at
Buy Calvin Klein Women's CK One Cotton Lightly Lined Demi Bra, Mini Staggered Logo Print, 34D at Skjermer, lampeføtter og ledninger - IKEA
Skjermer, lampeføtter og ledninger - IKEA CACIQUE BRA SIZE 40D Black Floral Print Intuition Uplift Plunge
CACIQUE BRA SIZE 40D Black Floral Print Intuition Uplift Plunge How to Style a Floral Midi Skirt - 7 Outfit Ideas for Summer & Fall
How to Style a Floral Midi Skirt - 7 Outfit Ideas for Summer & Fall
