1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only. - ppt download
4.6 (238) In stock

3 Slope Stability In slope stability analysis we determine the Factor of Safety as a ratio of resisting forces to driving forces F s = Resisting / Driving Theoretically, any slope with a Factor of Safety less than one will fail and any slope with a factor of safety greater than one will not. Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data.
1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only
2 Slope Stability In general you have: Driving Force – Weight of Slope Resisting Force – Strength of soil along slip surface Buttress at toe W c
Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data..
4 Slope Stability Example of Circular Slip Surface (from geoslope software) Circular slip surfaces often used in analysis as the most likely approximated shape of the failure surface
5 Slope Stability Non circular slip surfaces can also be analyzed
Now: W n sin α (driving) N= W n cos α T r = shear face = c’ + F ’ tan φ’ (resisting) W n sinα W n cos α α.
7 Slope Stability Performing this analysis on each slice and then summing the components from each slice F s = Σ (c L + W cos α tan φ) / Σ (W sin α )
8 Slope Stability This analysis is very conducive to a tabular solution WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ8 + 9 F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)
9 Slope Stability - Example Each box is 5’ x 5’ * = 120 pcf c = 300 psf φ = 32 o
10 Slope Stability - Example First, Find the areas for each slice A1 A2 A3 A4
11 Slope Stability WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)

Slope Stability and Landslides » Geology Science

PDF) A practical procedure for the back analysis of slope failures in closely jointed rock masses

Ch10-Slope Stability Examples, PDF, Soil Mechanics

Mechanics of Materials [9th ed.]

Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Chapter 2 - Findings, Application of LRFD Bridge Design Specifications to High-Strength Structural Concrete: Shear Provisions
Rayleigh–Taylor unstable condensing liquid layers with nonlinear effects of interfacial convection and diffusion of vapour, Journal of Fluid Mechanics

Hydrogeologic characterization of Area B, Fort Detrick, Maryland
GM.1943-5622.0002292/asset/27326b68-27b1-45ab-a3fe-2e676814a357/assets/images/large/figure1.jpg)
Seismic Bearing Capacity of Geosynthetic Reinforced Strip Footings Using Upper Bound Limit Analysis, International Journal of Geomechanics
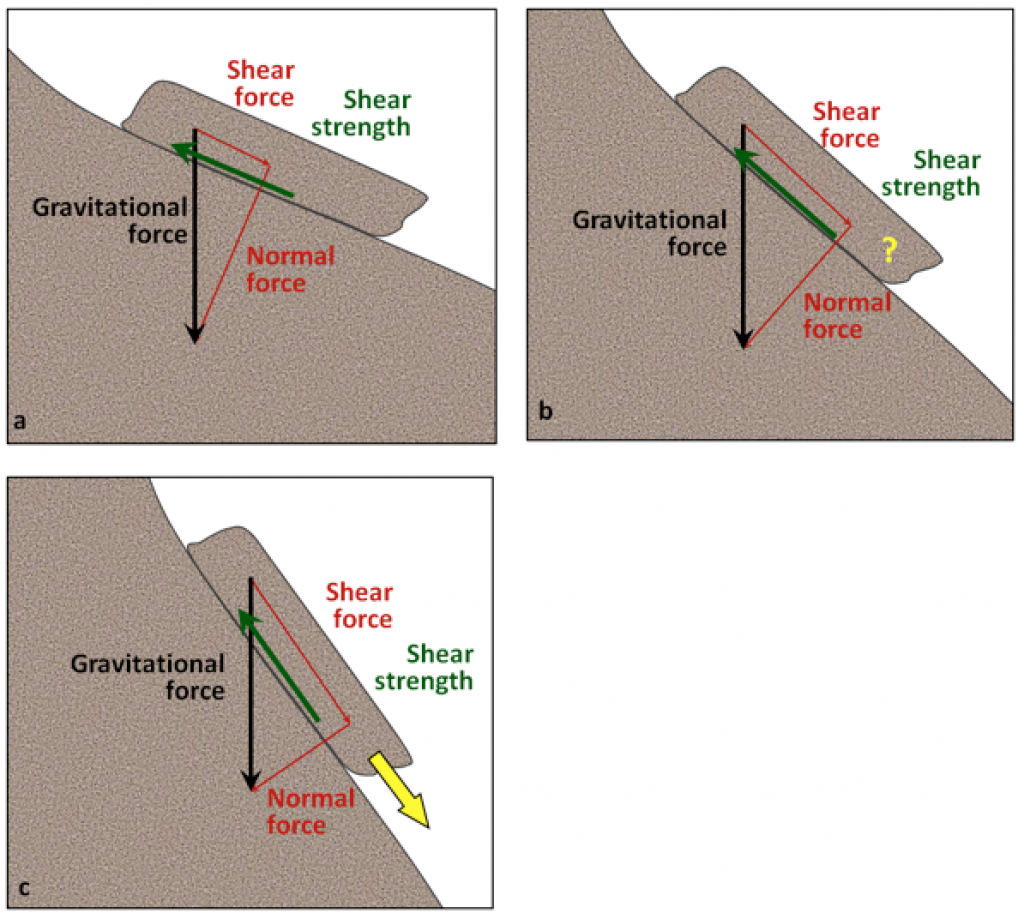
15.1 Factors That Control Slope Stability – Physical Geology – 2nd Edition
Schematic of the entry and exit slip surface (from SLOPE/W manual).
Slope Stability - Slope stability analysis with slip surface circular or polygonal
Journal of the Virtual Explorer A dynamic review electronic
Critical slip surface for the slope reinforced with one row of
 VETEMENTS Tan Logo Monogram Tights Vetements
VETEMENTS Tan Logo Monogram Tights Vetements Ladivine CD928 Long Lace Mermaid Wedding Dress Plunging Neckline Bridal Gown
Ladivine CD928 Long Lace Mermaid Wedding Dress Plunging Neckline Bridal Gown Rescued black leopard dies; wildlife officials yet to determine
Rescued black leopard dies; wildlife officials yet to determine Fabletics, Pants & Jumpsuits
Fabletics, Pants & Jumpsuits 2023 Bowman Chrome Baseball Review – Sports Card Market
2023 Bowman Chrome Baseball Review – Sports Card Market Vassarette® Convertible T-Shirt Bra in a 2 pack
Vassarette® Convertible T-Shirt Bra in a 2 pack