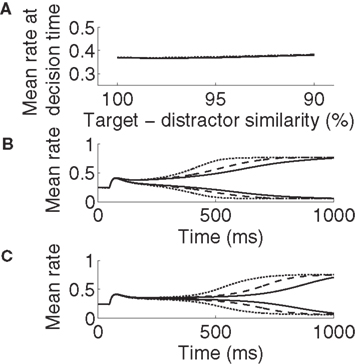
The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has
4.5 (485) In stock


The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has one
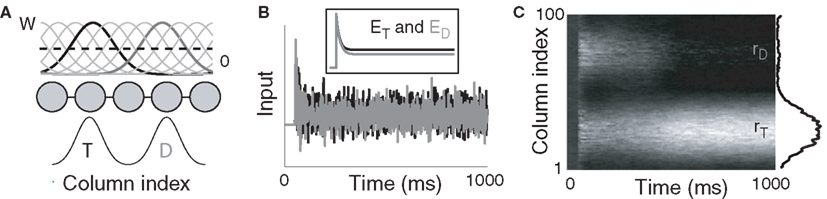
Frontiers Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

a and b. In figure a the estimated normal zone length between the

a and b. In figure a the estimated normal zone length between the
Michael C. Dorris's research works Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (CAS) and other places

Dominic STANDAGE, Marie Curie Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, School of Psychology

PDF) Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit
Frontiers Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

Dominic STANDAGE, Marie Curie Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, School of Psychology

PDF) Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equati

The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has one

Dominic STANDAGE, Marie Curie Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, School of Psychology

The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has one

Dominic STANDAGE, Marie Curie Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, School of Psychology
Steady-State Approximation, Rate Law, Kinetics - Chemistry
Steady-State Theory - Universe, FAQs
Want to Know More! Basics of Thermo-Fluid Analysis 18: Chapter 3
 Wool and mohair-blend drawstring pants
Wool and mohair-blend drawstring pants Buy Marks & Spencer Cool Comfort Cotton Rich Minimiser Bra C H In White
Buy Marks & Spencer Cool Comfort Cotton Rich Minimiser Bra C H In White Katie Austin's Go-To Fitness Brands for Top-Notch Workouts and
Katie Austin's Go-To Fitness Brands for Top-Notch Workouts and Denim Cargo Jogger Pants
Denim Cargo Jogger Pants LifeSource Vitamins - Melatonin - 5 mg. - supplement has shown to help with sleeping issues and ease jet lag, without the hazards or side effects of prescription sleeping pills.
LifeSource Vitamins - Melatonin - 5 mg. - supplement has shown to help with sleeping issues and ease jet lag, without the hazards or side effects of prescription sleeping pills. How Will Navi Mumbai Aerotropolis Create Demand For Housing?
How Will Navi Mumbai Aerotropolis Create Demand For Housing?