Substrate vibrations mediate behavioral responses via femoral
4.5 (442) In stock
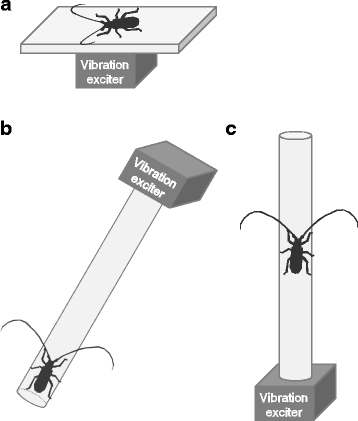
Background Vibrational senses are vital for plant-dwelling animals because vibrations transmitted through plants allow them to detect approaching predators or conspecifics. Little is known, however, about how coleopteran insects detect vibrations. Results We investigated vibrational responses of the Japanese pine sawyer beetle, Monochamus alternatus, and its putative sense organs. This beetle showed startle responses, stridulation, freezing, and walking in response to vibrations below 1 kHz, indicating that they are able to detect low-frequency vibrations. For the first time in a coleopteran species, we have identified the sense organ involved in the freezing behavior. The femoral chordotonal organ (FCO), located in the mid-femur, contained 60–70 sensory neurons and was distally attached to the proximal tibia via a cuticular apodeme. Beetles with operated FCOs did not freeze in response to low-frequency vibrations during walking, whereas intact beetles did. These results indicate that the FCO is responsible for detecting low-frequency vibrations and mediating the behavioral responses. We discuss the behavioral significance of vibrational responses and physiological functions of FCOs in M. alternatus. Conclusions Our findings revealed that substrate vibrations mediate behavioral responses via femoral chordotonal organs in M. alternatus.

Vibration detection in arthropods: Signal transfer, biomechanics

The auditory midbrain mediates tactile vibration sensing

Vibration-Induced Immobility in Coleopteran Insects
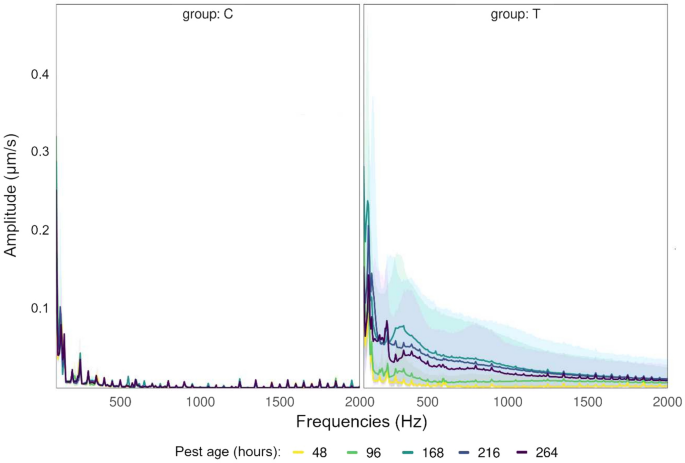
Detection and characterization of incidental vibrations from

Vibration detection in arthropods: Signal transfer, biomechanics

Communication by substrate-borne mechanical waves in insects: From basic to applied biotremology - ScienceDirect

Exploitation of Vibration Sensing for Pest Management in Longicorn Beetles
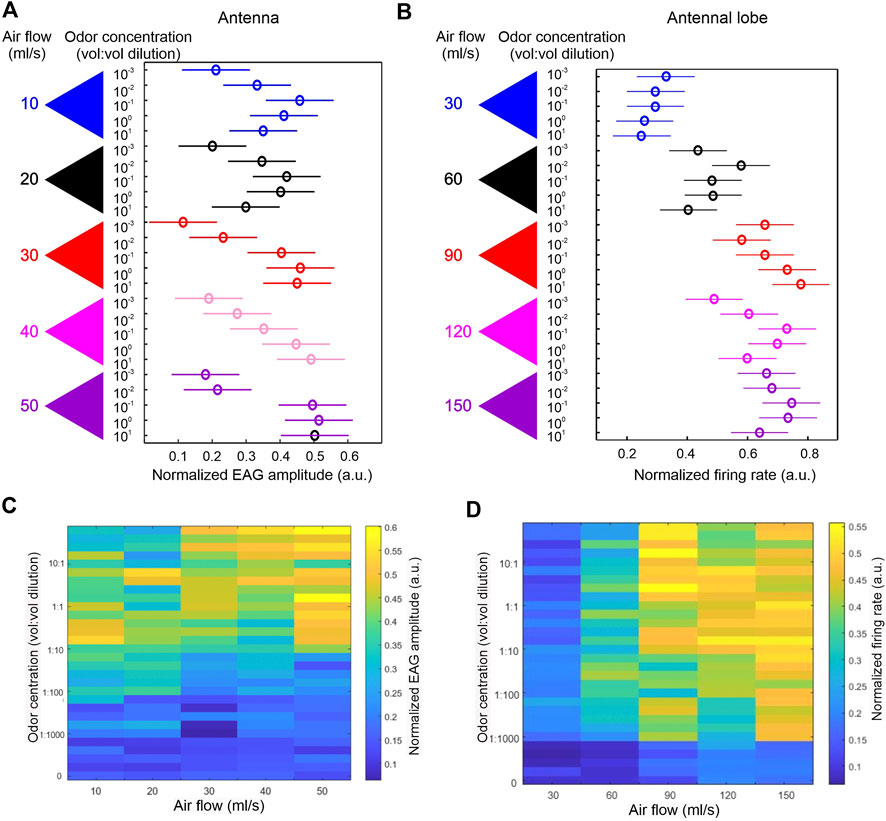
Frontiers Experimental and theoretical probe on mechano- and chemosensory integration in the insect antennal lobe

PDF) Physiology of vibration-sensitive afferents in the femoral

Central processing of leg proprioception in Drosophila

Communication by substrate-borne mechanical waves in insects: From basic to applied biotremology - ScienceDirect
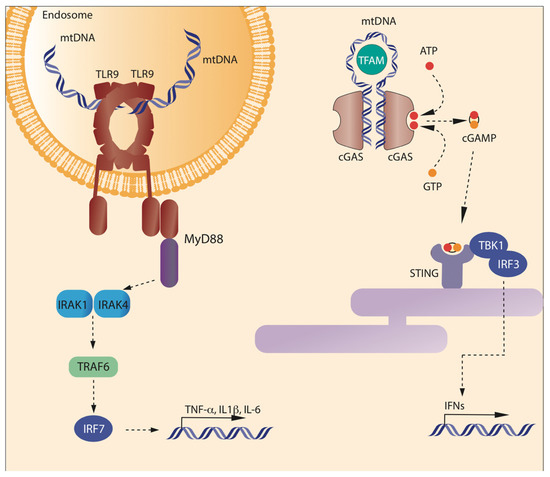
Cells, Free Full-Text
DEC219372 - DEMON SLAYER KIMETSU VIBRATION STARS TENGEN UZUI FIG
What is Random Vibration Testing? - Vibration Research
Naruto Shippuden Vibration Stars Pain Non-Scale Figure - Tokyo
Naruto Shippuden Vibration Stars Naruto Uzumaki Iii Fig from BANPRESTO – Big B Comics
 BALEAF Women's Sweatpants Joggers Cotton Yoga Lounge Sweat Pants
BALEAF Women's Sweatpants Joggers Cotton Yoga Lounge Sweat Pants Boobies Shapes Art Print by Mambo - Fy
Boobies Shapes Art Print by Mambo - Fy Empyre Tori Loose Fit Light Wash Denim Skate Shorts
Empyre Tori Loose Fit Light Wash Denim Skate Shorts Pokemon 124 Jynx Pokedex: Evolution, Moves, Location, Stats
Pokemon 124 Jynx Pokedex: Evolution, Moves, Location, Stats- $_1.JPG
 Womens Casual High Waist Pencil Pants Tapered Capris Elastic Waist Drawstring Cinch Bottom Trouser with Pockets Black at Women's Clothing store
Womens Casual High Waist Pencil Pants Tapered Capris Elastic Waist Drawstring Cinch Bottom Trouser with Pockets Black at Women's Clothing store